Since the early Middle Ages, the Baltic Sea has been an area of intense political, economic and cultural contacts. It was a time of both flourishing trade and economic and political rivalry. Connecting many parts of Europe, the Baltic Sea was the economic center of the Hanseatic League an economic alliance of the late Middle Ages, a federation of merchant cities from the 13th to the 17th century. In the 16th and early 17th centuries Poland, Sweden, and Denmark fought for influence in the Baltic Sea. In the 18th century, Russia and Prussia led the way in the Baltic Sea. The First World War was partly fought in the Baltic. During World War II, an important episode was a naval mine warfare, waged by all sides of the conflict. The Baltic waters, especially in the east, were full of explosives. Every year at the end of summer specialist units from Poland, Denmark, Estonia, the Netherlands, Lithuania and Germany go to sea to detect and neutralize unexploded ordnance.
Nine countries are located by the Baltic Sea: Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia, Poland, Germany; its drainage basin also includes: Norway, Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The area is home to more than 100 million people, producing nearly 15 percent of the world's output. 70,000 ships pass through the straits every year. To this must be added the fleet fishing in the Baltic Sea.
There are about 1000 ports and harbors on the Baltic Sea. The more important ports are: Szczecin, Gdansk, Gdynia, Copenhagen, Stockholm, Helsinki, St. Petersburg, Tallinn, Riga, Klaipeda, Kaliningrad, Rostock. The largest shipyards are: Copenhagen, Kiel, Rostock, Szczecin, Gdansk, St. Petersburg, Stockholm.
The Baltic Sea is biologically inferior to the North Sea or Atlantic fisheries, but all countries bordering the Baltic Sea catch fish. Particularly rapid increases in fishing occurred after World War II.
A considerable amount of fish caught by Poland comes from the Baltic Sea. From sea fish: herring, sprat, cod, several species of flatfish and of lesser utility importance: mackerel, belon, eel, sandeel. From migratory species: salmon, eel and less important in economic terms: whitefish or smelt. Freshwater fish have an important share in Baltic fisheries. To these species belong: perch, zander, pike, roach, bream and others.
Polish boats also fish in deep-sea fisheries.
On the coast – in Kołobrzeg, Szczecin, Gdańsk, Gdynia, Władysławowo – most fish processing plants are located.
The Baltic Sea is divided into sub-areas in terms of fishing grounds. The southern Baltic, i.e. our coastline, is numbered: 24 (Pomeranian Bay to Bornholm), 25 (from Pomeranian Bay to Władysławowo) and 26 (Gdansk Bay).
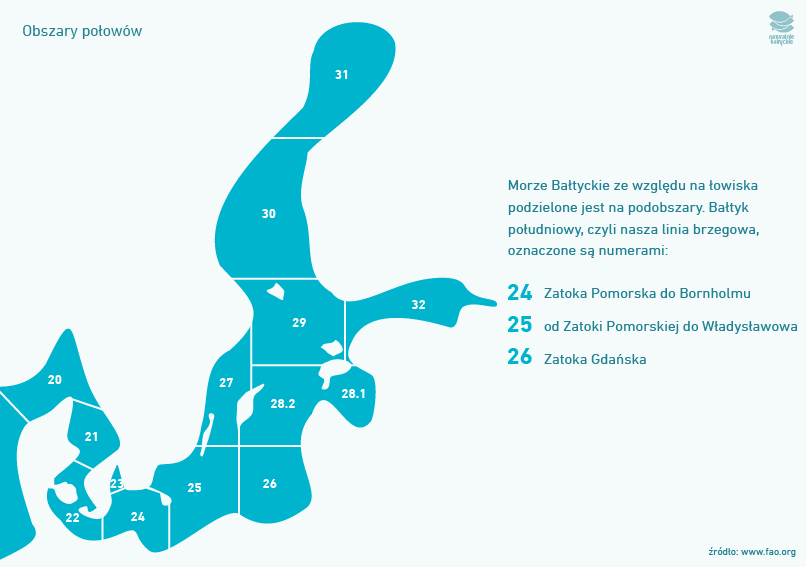
Map of the Baltic Sea showing the divisions between the Belts, the Sound and the Baltic Sea straits (source: http://www.fao.org/fishery/area/Area27/en)
The Baltic Sea is of great economic importance to Poland. It enables the development of sea transport and sea ports as urban centers. The largest share in the reloading of goods has the port complex of Szczecin-Swinoujście and Gdańsk-Gdynia. Ports in Kołobrzeg, Darłówek, Ustka and Elbląg are of local importance.
Ferry shipping is still popular. The most important ferry lines are connections Swinoujscie-Ystad and Swinoujscie-Malmoe (Swede.
The largest shipyards are located in Szczecin, Gdynia and Gdansk. The shipyards build and repair various types of ships (chemical, container, general cargo). In the territorial sea, which is 12 miles wide, and in the Polish economic zone, natural resources are prospected. Crude oil, potassium salt, amber, heavy minerals, e.g. zircon, have been found here. In the Baltic Sea, north of Wladyslawowo, there is a Polish drilling platform "Petrobaltic", which extracts oil from under the sea bed (about 200 thousand tonnes a year).
The Baltic Sea coast is an area of outstanding therapeutical, tourist and recreational values. These include: do
sandy beaches, dune walls, forests and iodine-rich air and mineral waters. The most famous tourist and holiday resorts on the Baltic Sea include: Sopot, Kołobrzeg, Łeba, Ustka, Świnoujście and Międzyzdroje.